Prof. Feng Ye / Prof. ZhengtuLi team from the First Affiliated Hospital of Guangzhou MedicalUniversity/Guangzhou Institute of Respiratory Health/State Key Laboratory of Respiratory Disease published their latest research findings in the internationally authoritative journal npj Biofilms and Microbiomes on November 13, 2024. The title of the research is "Impact of SARS-CoV-2 infection on respiratory and gut microbiome stability: a metagenomic investigation in long-term-hospitalized COVID-19 patients".

The research shows that there’s a mutual migration among COVID-19 patients’ intestinal and respiratory microorganisms. This kind of phenomenon is more prominent among critically ill patients and is one of the possible mechanisms for the occurrence of severe cases. These findings are expected to provide new ideas for the treatment and management of COVID-19. Meanwhile, they also emphasize the important role of the respiratory and intestinal microecology in infectious diseases.
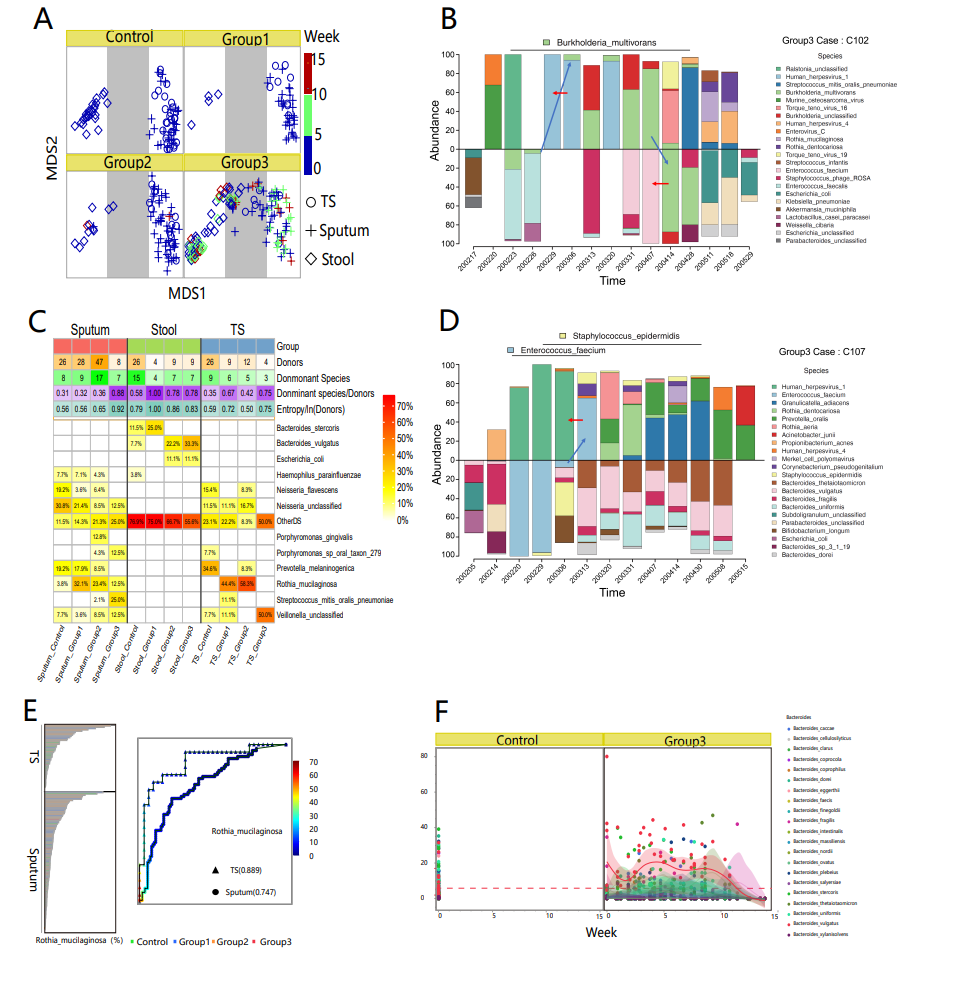
During the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic, the exploration of microecology has been essential for elucidating the intricacies of infection mechanisms and the recovery of afflicted individuals. To decipher the interplay of microorganisms between the intestinal and respiratory tracts, we collected sputum and throat swabs and feces from COVID-19 patients and explored the mutual migration among intestinal and respiratory microorganisms. Using next-generation sequencing (NGS) technology, we investigated intestinal and respiratory microorganism intermigration in two patients with severe COVID-19 during their hospitalization. Notably, we observed an expedited recovery of microecological equilibrium in one patient harboring Mycobacterium avium. Comparative analyses between 32 healthy controls and 110 COVID-19 patients with different disease severities revealed alterations in predominant microorganisms inhabiting the respiratory and intestinal tracts of COVID-19 patients. Among the alterations, intestinal Bacteroides vulgatus (BV) was identified as a noteworthy microorganism that exhibited marked enrichment in patients with severe COVID-19. BV, when highly abundant, may inhibit the transitional growth of Escherichia coli/Enterococcus, indirectly prevent the overgrowth of salivary streptococci, and maintain lung/intestinal microecology stability. In summary, this study elucidates the bidirectional microbial intermigration between the intestinal and respiratory tracts in COVID-19 patients. These findings are expected to provide new ideas for the treatment and management of COVID-19, underscoring the essential role of microecology in infectious diseases. Nevertheless, a systematic study of the roles of BV in recovery from infection is required to gain a deeper understanding of the mechanisms of microbial migration.
